

| Reference: | S40123 |
| Author | Pierre MARIETTE |
| Year: | 1646 ca. |
| Zone: | Turkey |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 490 x 375 mm |


| Reference: | S40123 |
| Author | Pierre MARIETTE |
| Year: | 1646 ca. |
| Zone: | Turkey |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 490 x 375 mm |
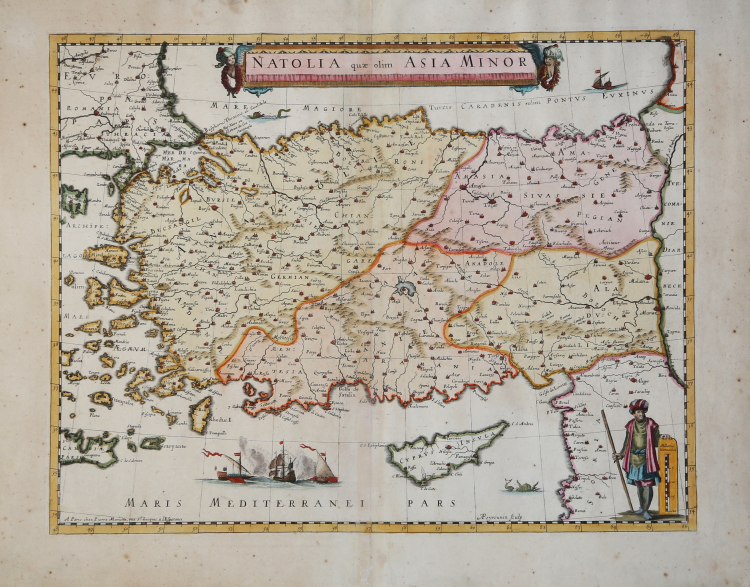
It covers Turkey from the Aegean Sea east as far as the Euphrates River. Cyprus and some of the Aegean Islands are also included. The map is beautifully detailed, noting several important towns, cities, rivers, and topography. Mountains are beautifully rendered in profile. The important cities of Constantinople (Istanbul), Smyrna (Izmir) and Antioch are identified.
The Ottoman Empire, at its peak, controlled the entire region during this period with Constantinople as its capital. In the middle part of the 17th century, after its period of growth, the Ottoman Empire would enter a period of gradual decline and stagnation.
Copper engraved map with fine colour, engraved by Abraham Peyrounin and published by “Pierre Mariette , rue St. Jacques a l’Esperance”, Paris c. 1650. Verso no text.
Uncommon plagiarism of Blaeu’s Natolia-Map (Koeman-v.d.Krogt 8110; Zacharakis/Scutari 388). It is well known, that Mariette commissioned Peyrounin from 1646 onwards to engrave copies of Dutch maps for his own publishing house (cf. Pastoureau, Les Atlas Francais, p. 345). But Pastoureau does not mention our map as an Atlas map. That is reason to believe, that our Mariette Natolia might be a single printed map.
Mariette's cartographic production derives mainly from the work of Nicolas Sanson, with whom Pierre Mariette "the old" and his son Pierre "the young" (1634-1716) collaborated in the famous Cartes Genèrales de toutes les parties du Monde.
Some maps, published at a later date, such as this one, directly by Mariette, are derived from different models; in this case the derivation from Dutch atlases is evident, given his collaboration with the Amsterdam publishers, in particular with Blaeu and Janssonius.
Copper engraving, finely hand-colored, in perfect condition. Rare.
Pierre MARIETTE (Parigi 1602 - 1658)
|
Mariette was born to a long-established and highly successful family of engravers, book publishers and printsellers in Paris. His father was Jean Mariette (1660–1742). In 1657 his father's father, Pierre Mariette (ii) (1634–1716), had bought the family business from his ailing father, Pierre Mariette (i) (1596–1657), for 30,000 livres. Family connections put him in contact as a young man with antiquarians such as the comte de Caylus, for whom Mariette would write his Lettre sur Leonardo da Vinci, printed as a preface to Caylus's book on Leonardo's caricatures, 1730. In 1722 he first met the immensely rich patron of the arts Pierre Crozat, whom he advised, whose collection he catalogued and from whose sale he purchased outstanding drawings. After he attended the Jesuit college in Paris, his father sent him on tour in 1717, to sharpen his connoisseurship and further family connections. First he went to Amsterdam, which was the center of the art trade, and then to Germany. In Vienna Mariette catalogued the art collection of Prince Eugene of Savoy. Everywhere the affable, curious and sociable Mariette made acquaintances and formed contacts with the scholarly and artistic community in Europe, which he maintained through correspondence. Through his artistic connections, Mariette was named a member of the prestigious Accademia delle Arti del Disegno, Florence, in 1733. His knowledge of prints and his close friendship with Caylus and the artist Charles-Antoine Coypel secured him a position reorganizing the old master print collection of the Bibliothèque Royale. In 1741 Mariette was asked to write the sale catalogue of Crozat's collection of paintings and antiquities, the first example of the modern descriptive sale catalogue. He purchased some of Crozat's drawings at the sale himself; a provenance from Mariette's collection, with its discrete collector's stamp, adds allure even to great Old Master drawings. Mariette engraved and printed several plates, an aspect of the family business. His engravings illustrated the Cours d'architecture qui comprend les ordres de Vignole ä ceux de Michel-Ange of Augustin-Charles d'Aviler (Paris, 1760), Before the death of his father in 1742, Mariette had already been running the family publishing and print-making business, an aspect of his career often overlooked by art historians. The firm had published Pierre Fauchard's Le chirurgien dentiste, ou traité des dents 1728, the first modern work on dentistry and a milestone of medical history. By 1750 he sold the family business that he had inherited in 1744, in order to purchase the office of Contrôleur Général de la Grande Chancellerie, a sinecure that allowed him to devote the rest of his life to his researches and to increasing his celebrated collection. He concentrated on prints and drawings, but also included paintings, bronzes and terracottas. Among his great drawings was a Michelangelo study of a nude for the Sistine Chapel. He shared Crozat's taste for the drawings of Rubens: at Crozat's sale he purchased sixty-two of the finest for his own collection. When his collections were dispersed at auction after his death, 1266 drawings were acquired by the Crown; they now form part of the collection at the Bibliothèque nationale. The albums of more than 3500 prints mounted on fine paper, which had been begun by his father, Jean Mariette, passed into the collection of the Earls Spencer. These "Spencer Albums" of Mariette's prints are one of the most important acquisitions made by the Harvard University Art Museums in recent years. The albums include etchings and engravings in a near-perfect state of preservation by Italian, Dutch, and Flemish printmakers, including Jacques Callot, Jusepe de Ribera, and Adriaen van Ostade.
Mariette also collected contemporary French paintings, Although he was immune to the forceful realism of Chardin, the more sentimental charm of Greuze found a place on his walls: Greuze's Young Peasant Boy, shown at the Salon of 1763 had already been purchased by Mariette, together with its pendant, before it was exhibited.
Mariette's further published works were not many. In 1750 he published a Traité historique des pierres gravées du Cabinet du Roi, on the hardstone carvings in the royal collection. His reputation as a connoisseur, who laid down the principles by which the hands of Italian master drawings could be ascertained, led to him being made an associate, then an honorary (1757) member of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture.
In 1764-65 he got into a public dispute in the pages of the Gazette littéraire de l'Europe with Giovanni Battista Piranesi, whom Mariette admired greatly as an artist, over Piranesi's polemical stand that the magnificence of Roman art derived from its Etruscan roots, rather than from its Greek borrowings.
Mariette's circle of friends was large, included Andre-Charles Boulle and was broad enough to define the state of art connoisseurship in France during his time, beginning with the circle he met at the houses of the prodigious collection Pierre-Antoine Crozat, where besides artists like Antoine Watteau and the classicizing sculptor Edmé Bouchardon, Mariette met the abbé de Maroulle and the comte de Caylus, who helped sharpen his eye.
Mariette married Angélique-Catherine Doyen in 1724. He acquired a country house at Croissy, which he named "Le Colifichet" was ennobled during the reign of Louis XV, and honored with the Order of the Saint-Esprit.
|
Pierre MARIETTE (Parigi 1602 - 1658)
|
Mariette was born to a long-established and highly successful family of engravers, book publishers and printsellers in Paris. His father was Jean Mariette (1660–1742). In 1657 his father's father, Pierre Mariette (ii) (1634–1716), had bought the family business from his ailing father, Pierre Mariette (i) (1596–1657), for 30,000 livres. Family connections put him in contact as a young man with antiquarians such as the comte de Caylus, for whom Mariette would write his Lettre sur Leonardo da Vinci, printed as a preface to Caylus's book on Leonardo's caricatures, 1730. In 1722 he first met the immensely rich patron of the arts Pierre Crozat, whom he advised, whose collection he catalogued and from whose sale he purchased outstanding drawings. After he attended the Jesuit college in Paris, his father sent him on tour in 1717, to sharpen his connoisseurship and further family connections. First he went to Amsterdam, which was the center of the art trade, and then to Germany. In Vienna Mariette catalogued the art collection of Prince Eugene of Savoy. Everywhere the affable, curious and sociable Mariette made acquaintances and formed contacts with the scholarly and artistic community in Europe, which he maintained through correspondence. Through his artistic connections, Mariette was named a member of the prestigious Accademia delle Arti del Disegno, Florence, in 1733. His knowledge of prints and his close friendship with Caylus and the artist Charles-Antoine Coypel secured him a position reorganizing the old master print collection of the Bibliothèque Royale. In 1741 Mariette was asked to write the sale catalogue of Crozat's collection of paintings and antiquities, the first example of the modern descriptive sale catalogue. He purchased some of Crozat's drawings at the sale himself; a provenance from Mariette's collection, with its discrete collector's stamp, adds allure even to great Old Master drawings. Mariette engraved and printed several plates, an aspect of the family business. His engravings illustrated the Cours d'architecture qui comprend les ordres de Vignole ä ceux de Michel-Ange of Augustin-Charles d'Aviler (Paris, 1760), Before the death of his father in 1742, Mariette had already been running the family publishing and print-making business, an aspect of his career often overlooked by art historians. The firm had published Pierre Fauchard's Le chirurgien dentiste, ou traité des dents 1728, the first modern work on dentistry and a milestone of medical history. By 1750 he sold the family business that he had inherited in 1744, in order to purchase the office of Contrôleur Général de la Grande Chancellerie, a sinecure that allowed him to devote the rest of his life to his researches and to increasing his celebrated collection. He concentrated on prints and drawings, but also included paintings, bronzes and terracottas. Among his great drawings was a Michelangelo study of a nude for the Sistine Chapel. He shared Crozat's taste for the drawings of Rubens: at Crozat's sale he purchased sixty-two of the finest for his own collection. When his collections were dispersed at auction after his death, 1266 drawings were acquired by the Crown; they now form part of the collection at the Bibliothèque nationale. The albums of more than 3500 prints mounted on fine paper, which had been begun by his father, Jean Mariette, passed into the collection of the Earls Spencer. These "Spencer Albums" of Mariette's prints are one of the most important acquisitions made by the Harvard University Art Museums in recent years. The albums include etchings and engravings in a near-perfect state of preservation by Italian, Dutch, and Flemish printmakers, including Jacques Callot, Jusepe de Ribera, and Adriaen van Ostade.
Mariette also collected contemporary French paintings, Although he was immune to the forceful realism of Chardin, the more sentimental charm of Greuze found a place on his walls: Greuze's Young Peasant Boy, shown at the Salon of 1763 had already been purchased by Mariette, together with its pendant, before it was exhibited.
Mariette's further published works were not many. In 1750 he published a Traité historique des pierres gravées du Cabinet du Roi, on the hardstone carvings in the royal collection. His reputation as a connoisseur, who laid down the principles by which the hands of Italian master drawings could be ascertained, led to him being made an associate, then an honorary (1757) member of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture.
In 1764-65 he got into a public dispute in the pages of the Gazette littéraire de l'Europe with Giovanni Battista Piranesi, whom Mariette admired greatly as an artist, over Piranesi's polemical stand that the magnificence of Roman art derived from its Etruscan roots, rather than from its Greek borrowings.
Mariette's circle of friends was large, included Andre-Charles Boulle and was broad enough to define the state of art connoisseurship in France during his time, beginning with the circle he met at the houses of the prodigious collection Pierre-Antoine Crozat, where besides artists like Antoine Watteau and the classicizing sculptor Edmé Bouchardon, Mariette met the abbé de Maroulle and the comte de Caylus, who helped sharpen his eye.
Mariette married Angélique-Catherine Doyen in 1724. He acquired a country house at Croissy, which he named "Le Colifichet" was ennobled during the reign of Louis XV, and honored with the Order of the Saint-Esprit.
|