


| Reference: | S35103 |
| Author | Claudio DUCHET (Duchetti) |
| Year: | 1570 ca. |
| Zone: | Istanbul |
| Printed: | Rome |
| Measures: | 443 x 300 mm |



| Reference: | S35103 |
| Author | Claudio DUCHET (Duchetti) |
| Year: | 1570 ca. |
| Zone: | Istanbul |
| Printed: | Rome |
| Measures: | 443 x 300 mm |
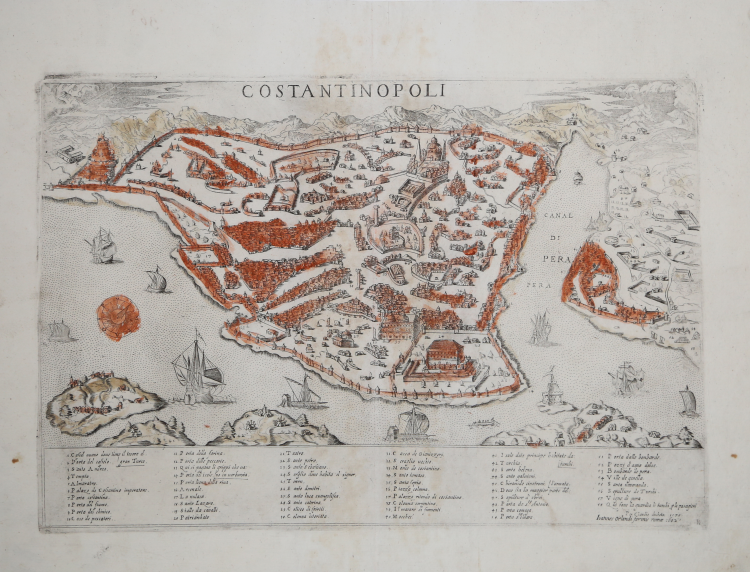
Bird’s eye view of the city engraved by Giacomo Franco for the publisher Claudio Duchetti, and printed in Venice around 1570.
Example in the second state, with the address of the publisher Giovanni Orlandi, printed in Roma in 1602.
At the top, below the upper border, is engraved the title: COSTANTINOPOLI. In the lower part of the plate, we find a numerical legend of 58 cross-references, divided into six columns. This is followed by the editorial imprint: Per Claudio ducheto 1570. Engraved in the lower right corner is the monogram composed of the interlaced letters IAF, identifying the engraver of the plate in Giacomo Franco. Orientation with a rose of sixteen winds in the sea, the northwest is at the top.
This is a derivation of the map published in Venice by Giovanni Andrea Vavassore and attributed to Giovanni Domenico Zorzi, circa 1520/30. Also known as Domenico delle Greche he lived in the then Constantinople for a period, beginning in 1525.
Zorzi-Vavassore's depiction of the city was to be the reference model taken up by all the mapss published in the 16th and 17th centuries. Some scholars speculate that for the drawing Vavassore may have been inspired by an earlier representation, now lost, perhaps by Florentine cartographer Francesco Roselli, or Venetian artist Gentile Bellini. It is also related to the manuscript map preserved in Düsseldorf, attributed to Buondelmonti, because both depict the city as it must have been toward the end of Mehmed II's reign, around 1480. Particularly striking are the coincidences in the depiction of the area outside the walls of Pera: in both plans there are cemeteries, canyons, fenced enclosures, and even written references such as "aguas frescas" or "vineyards of Pera." The two also reflect similar shipyards, docks, and arsenals in terms of location and type of activity. Vavassore also includes old and new palaces in his plan, defining elements of Ottoman power. However, he forgets some important mosques, such as Eyüp or Rum Mehmet Paşa, and instead fills the spaces with rows of buildings and a road network and incorporates erroneous elements, including a church about whose existence there is no historical evidence.
“Another derivation of the Vavassore map, engraved by Giacomo Franco for the publisher Claudio Duchetti. The work relates to Duchetti's Venetian period, before his return to Rome, where the second edition of the plate was printed. The numerical legend, compared to similar works before it, is enriched with a cross-reference (no. 58, Qui fano la guardia li turchi p li pasagieri). The work is listed in Antonio Lafreri's print shop catalog (no. 97) as "Constantinopoli". The plate was inherited by Giacomo Gherardi and is included in the catalog compiled for his widow, Quintilia Lucidi (Oct. 17-19, 1598, no. 420) described as "Constantinopoli Reale". It was then acquired, in 1602, by Giovanni Orlandi who reprinted it unaltered with only the addition of his own imprint. The plates were later sold to Francesco de Paoli, as documented by the inventory of the sale dated November 2, 1633. It is therefore possible the existence of a further drafting of the plate, of which, however, we have had no evidence" (cfr. Cartografia e topografia italiana del XVI secolo (2018), pp. 570-571).
Beautiful proof, printed on contemporary laid paper with watermark "anchor in the circle with star" and finely hand-colored at the time, with margins, in excellent condition.
Very rare work; only 4 institutional examples of this map are described in the census of Cartografia e topografia italiana del XVI secolo: Copenhagen, Universitetsbibliotekets; Fano, Federiciana; Malta, National Library; Paris, Bibliothèque Nationale.
Bibliografia
Bifolco-Ronca Cartografia e topografia italiana del XVI secolo (2018), pp. 570-571, tav. 172, I/II; Alberti (2010): n. 105; Borroni Salvadori (1980): n. 242; Destombes (1970): nn. 136-136a; Ganado (1994): VI, n. 49 & p. 215, n. 81; Phillips (1914): n. 87; Shirley (2004): II, n. 15; Tooley (1939): nn. 156-157.
Claudio DUCHET (Duchetti) (Attivo a Roma nella seconda metà del XVI sec.))
|
Print dealer and publisher.Active in Venice 1565-1572 and Rome.He was the brother of Francesco Duchetti and a nephew of Antonio Lafrery, inheriting half his plates.
Died 5 December 1585.He was buried in San Luigi dei Francesi.By the terms of his will, his brother –in-law Giacomo Gherardi was to run the business until the majority of Claudio’s son, Claudio.
While Gherardi in charge, he was to inscribe the prints ‘haeredes Claudii Duchetti’.
He commissioned plates from among others Perret, Thomassin and Brambilla.
The name 'Lafreri-School' is a widely used, but rather inaccurate, term used to describe a loose grouping of cartographers, mapmakers, engravers and publishers working in the twin centres of Rome and Venice, from about 1544 to circa 1585. Earlier this century, George Beans, a prominent American collector of Italian maps and atlases, proposed the alternative name 'I.A.T.O.' to describe the composite collections assembled and sold by this school - 'Italian, Assembled-To-Order'. While more apposite, it has failed to catch on with modern cataloguers and collectors. For the purposes of this article, I intend to refer to the cartographers, engravers and publishers involved as "the school", although even this term implies a greater structure and organisation than can currently be established. The principal reference source on the work of the school is R.V. Tooley's Maps in Italian Atlases of the Sixteenth Century (1). In his study, published in 1939, Tooley listed some 614 maps and plates (with variant states counted separately). Some were described from personal examination, others noted from secondary sources and listings. While now much out-dated, as more recent regional carto-bibliographies have effectively superceded particular sections, and new collections have come to light, it remains the only overview of the output of the school. The principal cartographer of the school was Giacomo Gastaldi (fl. 1542-1565), a Piedmontese who worked in Venice, becoming Cosmographer to the Venetian Republic. Karrow described him as "one of the most important cartographers of the sixteenth century. He was certainly the greatest Italian mapmaker of his age..." (2). While his achievement is obvious, it is hard to quantify. A large number of maps were published throughout this period with the geography credited to Gastaldi, but it is often difficult to know what role Gastaldi played in their creation. As a practice, he did not sign himself as publisher, although his name may be found in the title, dedication, or text to the reader. Frequently where there is no imprint one may assume that Gastaldi was the publisher. A further clue may be that many of the maps attributable to Gastaldi as publisher seem to have been engraved by Fabius Licinius. In other cases, where publication is credited to another, it is not always certain whether Gastaldi was commissioned by the publisher to compile the map, whether another less-enterprising publisher merely copied his work and attribution, or simply added Gastaldi's name in the title to add authority to the delineation. His name clearly commanded the same sort of respect that the Sanson name had in the last years of the seventeenth century, and as Guillaume de l'Isle's had in the first half of the eighteenth century. Paolo Forlani was a cartographer and engraver who worked in Venice between 1560 and circa 1571. The majority of his output was published under the imprint of other publishers, such as Giovanni Francesco Camocio, Ferrando Bertelli and Bolognini Zaltieri. In a pioneering study, David Woodward (4), by identifying Forlani's engraving style through various stages of development, has attributed a large number of previously unidentified maps to his hand, and provided a clearer picture of some of the publishing arrangements of the period. In the early 1560s Giovanni Francesco Camocio published a number of maps that were drawn by Forlani, including maps of the World, North Atlantic, Africa, France, Switzerland, and provinces of the Low Countries, to note but a few. Circa 1570, Camocio published an Isolario, or collection of maps of islands, principally from the Mediterranean, but including the British Isles and Iceland. Camocio's earliest issues lacked a title-page, and tended to be a relatively random selection from the available stock. Later he added a title Isole Famose Porti, Fortezze E Terre Maritime. After his death, which is assumed to have been in 1573, the plates were reprinted, with a title-page bearing the Bertelli family address 'alla Libraria del Segno di S. Marco', possibly by Donato Bertelli, whose imprint is found on a later state of Camocio's world map of 1560. The largest grouping was the Bertelli family. The most active was Ferrando Bertelli, who flourished in the 1560's and 1570's, but maps from the last quarter of the seventeenth century are known with the imprints of Andrea, Donato, Lucca, Nicolo and Pietro. Again, a number of maps published by Ferrando were drawn or engraved by Forlani.
Antonio Salamanca (1500 – 1562) settled in Rome his chalcographical business; his activity was then carried on and enlarged by his scholar Antonio Lafrery (1512 – 1577), and then by his grand son Claudio Duchet (Duchetti), Giovanni Orlandi, Henrik van Schoel, and finally by De Rossi. In Venice, the most important centre of map production, he was initiated into engraving by Giovanni Andrea Vavassore and Matteo Pagano, who had worked with Giacomo Gastaldi, the most important European cartographer of the XVI century. Other important exponents of the Venetian chalcography were Fabio Licinio, Fernando Bertelli, Giovanni Francesco Camocio and above all of them Paolo Forlani. Although he’s better known as publisher of Roman archeology, Antoine de Lafrery, born in France, has been the publisher thathas given the biggest impulse to Roman chalcography, becoming in a few years an expert seller as well. For that reason, even though he’s not the one that has published most maps in his time, all the chalcographic works printed in Rome and Venice during the XVI century are nowadays defined as “charts of lafrerian school”. This definition was given by Adolf Erik Nordenskiold, one of the fathers of the history of cartography, who also introduced the definition of Lafrery Atlas, talking about charts printed in Rome and published by Lafrery, in which we find a sort of title page with the title Tavole moderne de geografia secondo l’ordine di Tolomeo. Lafrery’s school produced a huge amount of maps, usually selling them as separate charts and somehow and then edited in a bigger volume. Since the charts had all different measures, the artists needed to trim them with copper to get them to the same size, adding at the end estra pieces of paper, if necessary.
|
Claudio DUCHET (Duchetti) (Attivo a Roma nella seconda metà del XVI sec.))
|
Print dealer and publisher.Active in Venice 1565-1572 and Rome.He was the brother of Francesco Duchetti and a nephew of Antonio Lafrery, inheriting half his plates.
Died 5 December 1585.He was buried in San Luigi dei Francesi.By the terms of his will, his brother –in-law Giacomo Gherardi was to run the business until the majority of Claudio’s son, Claudio.
While Gherardi in charge, he was to inscribe the prints ‘haeredes Claudii Duchetti’.
He commissioned plates from among others Perret, Thomassin and Brambilla.
The name 'Lafreri-School' is a widely used, but rather inaccurate, term used to describe a loose grouping of cartographers, mapmakers, engravers and publishers working in the twin centres of Rome and Venice, from about 1544 to circa 1585. Earlier this century, George Beans, a prominent American collector of Italian maps and atlases, proposed the alternative name 'I.A.T.O.' to describe the composite collections assembled and sold by this school - 'Italian, Assembled-To-Order'. While more apposite, it has failed to catch on with modern cataloguers and collectors. For the purposes of this article, I intend to refer to the cartographers, engravers and publishers involved as "the school", although even this term implies a greater structure and organisation than can currently be established. The principal reference source on the work of the school is R.V. Tooley's Maps in Italian Atlases of the Sixteenth Century (1). In his study, published in 1939, Tooley listed some 614 maps and plates (with variant states counted separately). Some were described from personal examination, others noted from secondary sources and listings. While now much out-dated, as more recent regional carto-bibliographies have effectively superceded particular sections, and new collections have come to light, it remains the only overview of the output of the school. The principal cartographer of the school was Giacomo Gastaldi (fl. 1542-1565), a Piedmontese who worked in Venice, becoming Cosmographer to the Venetian Republic. Karrow described him as "one of the most important cartographers of the sixteenth century. He was certainly the greatest Italian mapmaker of his age..." (2). While his achievement is obvious, it is hard to quantify. A large number of maps were published throughout this period with the geography credited to Gastaldi, but it is often difficult to know what role Gastaldi played in their creation. As a practice, he did not sign himself as publisher, although his name may be found in the title, dedication, or text to the reader. Frequently where there is no imprint one may assume that Gastaldi was the publisher. A further clue may be that many of the maps attributable to Gastaldi as publisher seem to have been engraved by Fabius Licinius. In other cases, where publication is credited to another, it is not always certain whether Gastaldi was commissioned by the publisher to compile the map, whether another less-enterprising publisher merely copied his work and attribution, or simply added Gastaldi's name in the title to add authority to the delineation. His name clearly commanded the same sort of respect that the Sanson name had in the last years of the seventeenth century, and as Guillaume de l'Isle's had in the first half of the eighteenth century. Paolo Forlani was a cartographer and engraver who worked in Venice between 1560 and circa 1571. The majority of his output was published under the imprint of other publishers, such as Giovanni Francesco Camocio, Ferrando Bertelli and Bolognini Zaltieri. In a pioneering study, David Woodward (4), by identifying Forlani's engraving style through various stages of development, has attributed a large number of previously unidentified maps to his hand, and provided a clearer picture of some of the publishing arrangements of the period. In the early 1560s Giovanni Francesco Camocio published a number of maps that were drawn by Forlani, including maps of the World, North Atlantic, Africa, France, Switzerland, and provinces of the Low Countries, to note but a few. Circa 1570, Camocio published an Isolario, or collection of maps of islands, principally from the Mediterranean, but including the British Isles and Iceland. Camocio's earliest issues lacked a title-page, and tended to be a relatively random selection from the available stock. Later he added a title Isole Famose Porti, Fortezze E Terre Maritime. After his death, which is assumed to have been in 1573, the plates were reprinted, with a title-page bearing the Bertelli family address 'alla Libraria del Segno di S. Marco', possibly by Donato Bertelli, whose imprint is found on a later state of Camocio's world map of 1560. The largest grouping was the Bertelli family. The most active was Ferrando Bertelli, who flourished in the 1560's and 1570's, but maps from the last quarter of the seventeenth century are known with the imprints of Andrea, Donato, Lucca, Nicolo and Pietro. Again, a number of maps published by Ferrando were drawn or engraved by Forlani.
Antonio Salamanca (1500 – 1562) settled in Rome his chalcographical business; his activity was then carried on and enlarged by his scholar Antonio Lafrery (1512 – 1577), and then by his grand son Claudio Duchet (Duchetti), Giovanni Orlandi, Henrik van Schoel, and finally by De Rossi. In Venice, the most important centre of map production, he was initiated into engraving by Giovanni Andrea Vavassore and Matteo Pagano, who had worked with Giacomo Gastaldi, the most important European cartographer of the XVI century. Other important exponents of the Venetian chalcography were Fabio Licinio, Fernando Bertelli, Giovanni Francesco Camocio and above all of them Paolo Forlani. Although he’s better known as publisher of Roman archeology, Antoine de Lafrery, born in France, has been the publisher thathas given the biggest impulse to Roman chalcography, becoming in a few years an expert seller as well. For that reason, even though he’s not the one that has published most maps in his time, all the chalcographic works printed in Rome and Venice during the XVI century are nowadays defined as “charts of lafrerian school”. This definition was given by Adolf Erik Nordenskiold, one of the fathers of the history of cartography, who also introduced the definition of Lafrery Atlas, talking about charts printed in Rome and published by Lafrery, in which we find a sort of title page with the title Tavole moderne de geografia secondo l’ordine di Tolomeo. Lafrery’s school produced a huge amount of maps, usually selling them as separate charts and somehow and then edited in a bigger volume. Since the charts had all different measures, the artists needed to trim them with copper to get them to the same size, adding at the end estra pieces of paper, if necessary.
|