



| Reference: | S40058 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1693 ca. |
| Zone: | Astronomy |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 700 x 482 mm |



| Reference: | S40058 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1693 ca. |
| Zone: | Astronomy |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 700 x 482 mm |
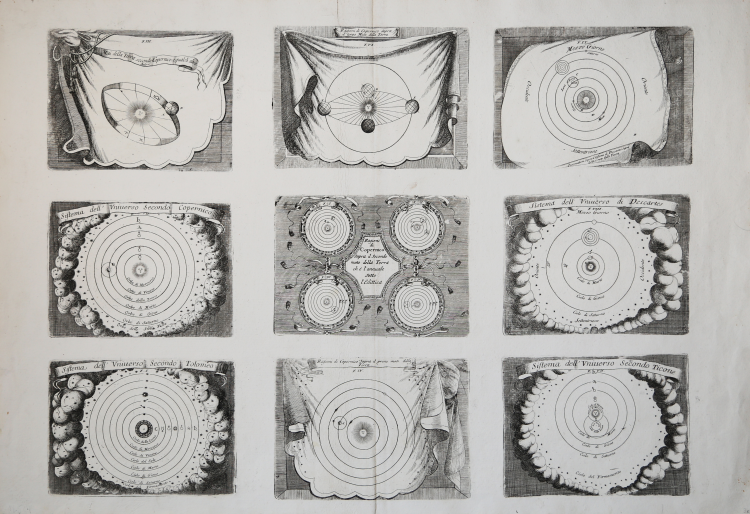
Sistema dell'universo secondo Tolomeo-Sistema dell'universo secondo Copernico-Moti della terra secondo Copernico-Ragioni di Copernico sopra il primo moto della terra-Sistema dell'universo secondo Ticone- Sistema dell'univeso di Descartes-Osservazioni sopra il sistema di Descartes.
Curious and very interesting plate, consisting of 9 small engravings, which represents a summary of the various concepts that had inflamed the seventeenth-century astronomical panorama. Coronelli illustrates the four "systems" which were hotly debated in his time, those of Copernicus, Descartes, and Tychonus and obviously the oldest, Ptolemy. The nine plates were prepared by the author for the Epitome Cosmografica of 1693; it is the work that represents the practical and theoretical synthesis of the vast work of cartographer that the author will play in his life (Ravenna 1650-Venice 1718).
The Epitome Cosmografica, dedicated to the Accademia degli Argonauti,, the first geographical society in the world, founded by Coronelli himself, is divided into three books, the first, of 35 chapters, focuses on astronomy and celestial cartography, the second, of 17 chapters, deals with the earth and geography, finally the third consists of 5 chapters of the first part "which contains the description of 'various globes, which so far have been made" and in the last 23 chapters of the second part "which contains the practice" of the construction of the globes. The volume was printed in Cologne on behalf of the Venetian publisher Andrea Poletti.
Sheet taken from the Corso Geografico Universale of 1698.
Coronelli lived a period of extraordinary editorial fecundity since 1689, when he had the chair of geography at the University at the Procuratie, with the publication, in 1690, of the first volume of the Atlante Veneto. In fact under the name of Atlante Veneto goes the entire collection of thirteen works composed over the next decade, from the Isolario to the Specchio del mare.
Copper engraving, magnificent proof, with full margins, in perfect condition.
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|