

| Reference: | S36901 |
| Author | John SENEX |
| Year: | 1721 |
| Zone: | Sicily |
| Printed: | London |
| Measures: | 585 x 500 mm |


| Reference: | S36901 |
| Author | John SENEX |
| Year: | 1721 |
| Zone: | Sicily |
| Printed: | London |
| Measures: | 585 x 500 mm |
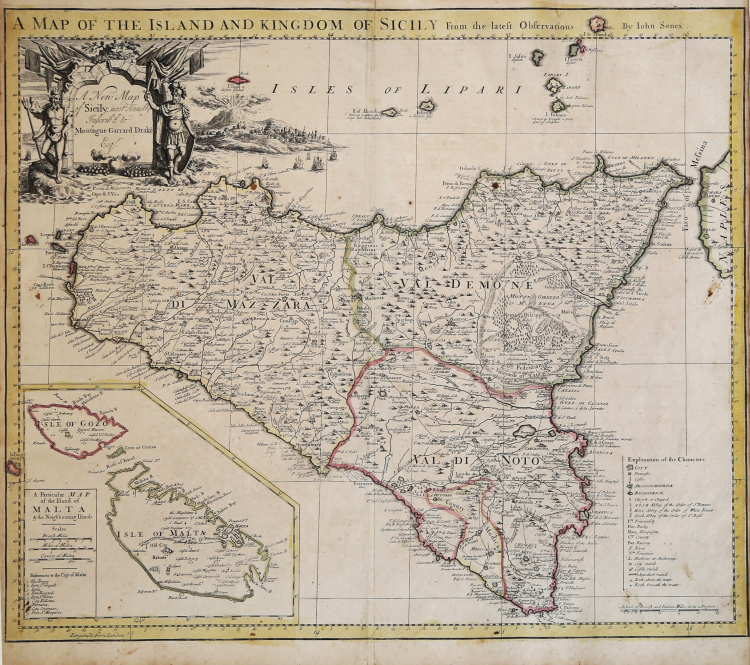
Striking and highly detailed map of Sicily, with a large inset of Malta.
Both the map and vignette next to the cartouche show Mt. Aetna erupting.
This highly detailed map includes towns, roads, rivers, mountains, bays, islands and a number of other features identified in the key in the lower right side of the image.
One of the most decorative and interesting large format English maps of Sicily published in the 18th century.
Etching, with original colour, good condition.
|
Sicilia 1477-1861 - La collezione Spagnolo- Patermo, n. 197.
|
John SENEX (Londra, 1678 – 1740)
|
John Senex (1678 - 1740) was one of the most important English map makers and publishers of the first half of the 18th century. He was first apprenticed to the prominent bookseller and publisher Robert Clavell, but his association with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price led him to a career as a surveyor, cartographer, globe maker, and map publisher and seller. His contribution to the development of the British map trade was such that he was honored (1728) by election to membership in the Royal Society, sponsored by some of the greatest scientists of the period. His early career was relatively unhappy; the society with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price lasted only 3 years and ended in bankruptcy, in 1706. From then on, until about 1710, he worked only with Price, from whom he learned and refined the art of engraving. The two devoted themselves to the design of an atlas of the world, competing with that of rival Herman Moll. When the partnership ended, Senex worked on his own cartographic collection, which was published as The English Atlas (1714); it was one of the most successful atlases of the century, being reprinted until 1760. Senex also worked as a semi-official engraver for the Royal Society, for its printer William Taylor, and for prominent figures within it, including Edmund Halley and William Whiston. He then published several important scientific maps, most notably Halley and Whiston's eclipse maps (1715 and 1724). These scientific contacts of his provided him with essential and innovative technical elements, useful for his wide range of terrestrial and celestial globes. With this solid foundation, Senex became the most prestigious map publisher of the time. Upon his death (1740) the printing press was directed by his widow Mary, who continued the business until 1755, when she retired; William Herbert and Robert Sayer acquired the rights to the cartographic works, while James Ferguson took over the part dealing with globes.
|
|
Sicilia 1477-1861 - La collezione Spagnolo- Patermo, n. 197.
|
John SENEX (Londra, 1678 – 1740)
|
John Senex (1678 - 1740) was one of the most important English map makers and publishers of the first half of the 18th century. He was first apprenticed to the prominent bookseller and publisher Robert Clavell, but his association with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price led him to a career as a surveyor, cartographer, globe maker, and map publisher and seller. His contribution to the development of the British map trade was such that he was honored (1728) by election to membership in the Royal Society, sponsored by some of the greatest scientists of the period. His early career was relatively unhappy; the society with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price lasted only 3 years and ended in bankruptcy, in 1706. From then on, until about 1710, he worked only with Price, from whom he learned and refined the art of engraving. The two devoted themselves to the design of an atlas of the world, competing with that of rival Herman Moll. When the partnership ended, Senex worked on his own cartographic collection, which was published as The English Atlas (1714); it was one of the most successful atlases of the century, being reprinted until 1760. Senex also worked as a semi-official engraver for the Royal Society, for its printer William Taylor, and for prominent figures within it, including Edmund Halley and William Whiston. He then published several important scientific maps, most notably Halley and Whiston's eclipse maps (1715 and 1724). These scientific contacts of his provided him with essential and innovative technical elements, useful for his wide range of terrestrial and celestial globes. With this solid foundation, Senex became the most prestigious map publisher of the time. Upon his death (1740) the printing press was directed by his widow Mary, who continued the business until 1755, when she retired; William Herbert and Robert Sayer acquired the rights to the cartographic works, while James Ferguson took over the part dealing with globes.
|