

| Reference: | S38014 |
| Author | John SENEX |
| Year: | 1712 |
| Zone: | Central Italy |
| Printed: | London |
| Measures: | 605 x 465 mm |


| Reference: | S38014 |
| Author | John SENEX |
| Year: | 1712 |
| Zone: | Central Italy |
| Printed: | London |
| Measures: | 605 x 465 mm |
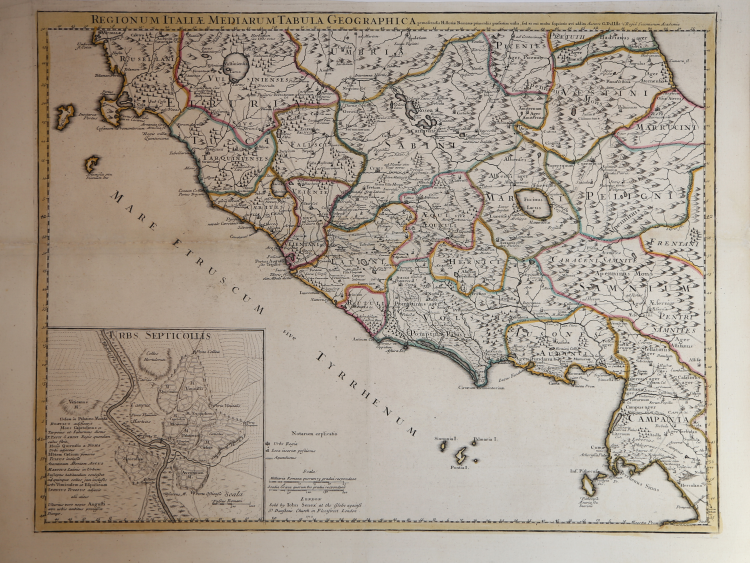
Regionum Italiae Mediarum tabula geographica pernoscendis Historiae Romanae primordiis praesertim utilis, sed et cui multa sequioris aevi addita. Auctore G. del'Isle, Regia Scientarum Academia.
At lower left the imprint: London Sold by Iohn Senex at the Globe against S. Dunstans Church in Fleetstreet London.
A rare English edition of Guillaume de l'Isle's map detailed map of the area of central eastern Italy around Rome, showing the regions in ancient times and including an inset map showing the seven hills of Rome.
John Senex (1678 - 1740) was one of the most important English map makers and publishers of the first half of the 18th century. He was first apprenticed to the prominent bookseller and publisher Robert Clavell, but his association with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price led him to a career as a surveyor, cartographer, globe maker, and map publisher and seller. His contribution to the development of the British map trade was such that he was honored (1728) by election to membership in the Royal Society, sponsored by some of the greatest scientists of the period. His early career was relatively unhappy; the society with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price lasted only 3 years and ended in bankruptcy, in 1706. From then on, until about 1710, he worked only with Price, from whom he learned and refined the art of engraving. The two devoted themselves to the design of an atlas of the world, competing with that of rival Herman Moll. When the partnership ended, Senex worked on his own cartographic collection, which was published as The English Atlas (1714); it was one of the most successful atlases of the century, being reprinted until 1760. Senex also worked as a semi-official engraver for the Royal Society, for its printer William Taylor, and for prominent figures within it, including Edmund Halley and William Whiston. He then published several important scientific maps, most notably Halley and Whiston's eclipse maps (1715 and 1724). These scientific contacts of his provided him with essential and innovative technical elements, useful for his wide range of terrestrial and celestial globes. With this solid foundation, Senex became the most prestigious map publisher of the time. Upon his death (1740) the printing press was directed by his widow Mary, who continued the business until 1755, when she retired; William Herbert and Robert Sayer acquired the rights to the cartographic works, while James Ferguson took over the part dealing with globes.
Copperplate with original colouring, good condition.
John SENEX (Londra, 1678 – 1740)
|
John Senex (1678 - 1740) was one of the most important English map makers and publishers of the first half of the 18th century. He was first apprenticed to the prominent bookseller and publisher Robert Clavell, but his association with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price led him to a career as a surveyor, cartographer, globe maker, and map publisher and seller. His contribution to the development of the British map trade was such that he was honored (1728) by election to membership in the Royal Society, sponsored by some of the greatest scientists of the period. His early career was relatively unhappy; the society with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price lasted only 3 years and ended in bankruptcy, in 1706. From then on, until about 1710, he worked only with Price, from whom he learned and refined the art of engraving. The two devoted themselves to the design of an atlas of the world, competing with that of rival Herman Moll. When the partnership ended, Senex worked on his own cartographic collection, which was published as The English Atlas (1714); it was one of the most successful atlases of the century, being reprinted until 1760. Senex also worked as a semi-official engraver for the Royal Society, for its printer William Taylor, and for prominent figures within it, including Edmund Halley and William Whiston. He then published several important scientific maps, most notably Halley and Whiston's eclipse maps (1715 and 1724). These scientific contacts of his provided him with essential and innovative technical elements, useful for his wide range of terrestrial and celestial globes. With this solid foundation, Senex became the most prestigious map publisher of the time. Upon his death (1740) the printing press was directed by his widow Mary, who continued the business until 1755, when she retired; William Herbert and Robert Sayer acquired the rights to the cartographic works, while James Ferguson took over the part dealing with globes.
|
John SENEX (Londra, 1678 – 1740)
|
John Senex (1678 - 1740) was one of the most important English map makers and publishers of the first half of the 18th century. He was first apprenticed to the prominent bookseller and publisher Robert Clavell, but his association with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price led him to a career as a surveyor, cartographer, globe maker, and map publisher and seller. His contribution to the development of the British map trade was such that he was honored (1728) by election to membership in the Royal Society, sponsored by some of the greatest scientists of the period. His early career was relatively unhappy; the society with Jeremiah Seller and Charles Price lasted only 3 years and ended in bankruptcy, in 1706. From then on, until about 1710, he worked only with Price, from whom he learned and refined the art of engraving. The two devoted themselves to the design of an atlas of the world, competing with that of rival Herman Moll. When the partnership ended, Senex worked on his own cartographic collection, which was published as The English Atlas (1714); it was one of the most successful atlases of the century, being reprinted until 1760. Senex also worked as a semi-official engraver for the Royal Society, for its printer William Taylor, and for prominent figures within it, including Edmund Halley and William Whiston. He then published several important scientific maps, most notably Halley and Whiston's eclipse maps (1715 and 1724). These scientific contacts of his provided him with essential and innovative technical elements, useful for his wide range of terrestrial and celestial globes. With this solid foundation, Senex became the most prestigious map publisher of the time. Upon his death (1740) the printing press was directed by his widow Mary, who continued the business until 1755, when she retired; William Herbert and Robert Sayer acquired the rights to the cartographic works, while James Ferguson took over the part dealing with globes.
|