

| Reference: | MMS1829 |
| Author | Domenico De ROSSI |
| Year: | 1691 |
| Zone: | Italy |
| Printed: | Rome |
| Measures: | 850 x 575 mm |


| Reference: | MMS1829 |
| Author | Domenico De ROSSI |
| Year: | 1691 |
| Zone: | Italy |
| Printed: | Rome |
| Measures: | 850 x 575 mm |
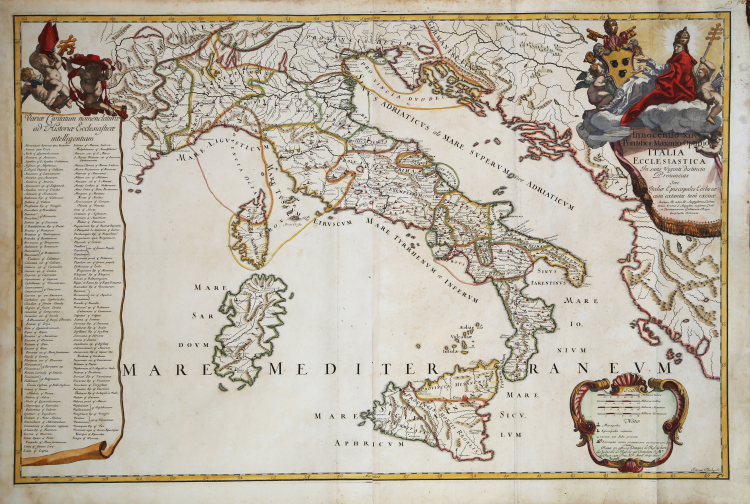
Large geographical and ecclesiastical map, depicting Italy with subdivisions by Augustinian fathers.
The map of Italy is derived from that of Father Augustin Lubin, published in 1649.
Dedicated by publisher Domenico de Rossi to Pope Innocent XII (at upper right - INNOCENTIO XII PONTIFICI MAXIMO OPTIMO ITALIA ECCLESIASTICA IN SUAS VIGINTI DISTINCTA PROVINCIAS SIVE ITALIAE EPISCOPALES ECCLESIAE CUM EXTANTES TUM EXCISAE) and engraved by Antonio Barbey.
The map is taken from Mercurio geografico overo Guida Geografica in tutte le parti del Mondo conforme le Tavole Geografiche del Sansone Baudran de Cantelli Data in luce con direttione, e cura di Gio. Giacomo de Rossi nella sua stamperia collection of maps published in Rome between 1660 and 1730 by the typography De Rossi - the date of the maps goes from 1669 to 1715 - whose first edition is due to Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. Over the years the atlas was enriched by an increasing number of maps in subsequent editions edited first by Domenico de Rossi and then by his son Filippo.
The Mercurio Geografico is a collection that brings together works by cartographers such as Michele Antonio Baudrand, Nicolas Sanson, Augustin Lubin, Filippo Titi, Giacomo Ameti, Giovanni Antonio Magini and Innocenzo Mattei, and which includes as its main "corpus" the great production of the geographer Giacomo Cantelli da Vignola. The maps are finely copied and engraved by the major engravers of the time including Falda, Widman, Barbey, Widman, Lhuillier, Donia, Mariotti.
Father Augustin Lubin (1624-1695) was an Augustinian humanist and theologian originally from Paris; author of important historical and geographical works that earned him the title of Geographer to the King. Famous for his work Orbis Augustinianus sive Conventuum Ordinis Eremitarum Sancti Augustini Chorographica et Topographica descriptio, published in Paris by Peter Baudouyn in 1659. The work produced by Lubin is very similar in its conception, to that produced by the Franciscans in 1649 and is intended to depict the provinces in which the Augustinian order is present, with the location of the convents.
The engraver Antonio Barbey, active in Rome in the second half of the 17th century, left studies of architecture and maps (cf. Petrucci C.A., Catalogo delle stampe della calcografia nazionale, Roma, 1953, p. 19). The members of the de Rossi family earned a reputation more than for engraving for print publications. When they ceased activity in 1732 the collection of their branches went to form the initial nucleus of the papal chalcography (cf. De Witt A., La collezione delle stampe della Galleria degli Uffizi, Rome, 1938, pp. 68-69).
Copper engraving, fine later hand colour, in good condition.
Literature
cfr. R. Almagià, Studi storici di cartografia napoletana, in “Archivio storico per le province napoletane”, 38 (1913), p. 645; A. Bonazzi, Il Mercurio geografico: il gioco e la differenza, in “Giacomo Cantelli: geografo del Serenissimo”, Bologna, 1995, p. 37-44 e 150-152; Bagrow 268; Phillips I 254-255; Shirley BL I, pp. 868-874.
Domenico De ROSSI (Roma 1647 - 1729)
|
Towards the end of the sixteenth century began the editorial activity of Antonio De Rossi, who with his sons Giuseppe the Elder and Giulio, founded the printing house that, over the next two centuries and through four generations, held the monopoly of chalcographic production in the city. The workshop had the sign “De Rossi alla Pace”. The history of the De Rossi family is characterized by internal disputes and contrasts that lead to the opening of individual printing houses in competition with each other. Giulio De Rossi's sons, Giuseppe the Younger and Giovanni Battista, nephews of Giuseppe De Rossi the Elder, had founded in 1628 their own workshop in the vicinity - at the corner of Via di Parione and Via della Pace near the church of S. Biagio della Fossa - but in 1635 Giovanni Battista in turn separated from his brother and opened a workshop in Piazza Navona, the third of the family. In 1644, after the death of Giuseppe the Younger, his brother Giovanni Battista became the most direct competitor of his uncle's workshop, the De Rossi alla Pace, now run by his widow along with their children who were then partly still minors [Sons of Giuseppe De Rossi the Elder (1560-1639) and Flaminia Fabio were Giovanni Domenico (1619-1653) Girolamo (born in 1621), Giovanni Giacomo (1627-1691) and Filippo (1631-1656)]. In 1648 Giovanni Giacomo De Rossi, son of Giuseppe, started his own activity in a workshop located “alla Pace”, with the contribution of about 800 plates inherited from his father, whose fund was divided among the four sons. At the death of his elder brother Giovanni Domenico (1653) the part of plates inherited from him was recovered by Giovanni Giacomo, who also took possession of many works of a geographical nature published by his brother. The corpus of works recovered by Giovanni Giacomo consisted of a collection that spanned a chronological span of more than a century, including part of the plates of Salamanca and Lafreri, the workshops of Adamo Scultori, Villamena, Maggi, Carenzano and many others. For the whole course of the century Giovanni Giacomo and his adopted son Domenico (1647-1729) were the point of reference of the Roman publishing industry and increased the chalcographic production of local and artistic character. In addition, in fact, to the works of Giovan Battista Falda we find in the list the engraving matrixes of painters-engravers such as Guido Reni, Giovan Benedetto Castiglione, Giovanni Andrea Podestà and Pietro Testa just to mention the main artists who relied on the De Rossi. When Domenico died in 1729, the printing house was inherited by his son Lorenzo Filippo, who immediately put it up for sale. Pope Clement XII forbade its sale abroad and ordered its appraisal with the intention of purchase by the Apostolic Chamber: the printing house was sold in March 1738 and formed the fund of the newly founded Calcografia Camerale. This act of sale is the document that witnesses the end of the De Rossi printing house, one of the most important European printing houses.
|
Domenico De ROSSI (Roma 1647 - 1729)
|
Towards the end of the sixteenth century began the editorial activity of Antonio De Rossi, who with his sons Giuseppe the Elder and Giulio, founded the printing house that, over the next two centuries and through four generations, held the monopoly of chalcographic production in the city. The workshop had the sign “De Rossi alla Pace”. The history of the De Rossi family is characterized by internal disputes and contrasts that lead to the opening of individual printing houses in competition with each other. Giulio De Rossi's sons, Giuseppe the Younger and Giovanni Battista, nephews of Giuseppe De Rossi the Elder, had founded in 1628 their own workshop in the vicinity - at the corner of Via di Parione and Via della Pace near the church of S. Biagio della Fossa - but in 1635 Giovanni Battista in turn separated from his brother and opened a workshop in Piazza Navona, the third of the family. In 1644, after the death of Giuseppe the Younger, his brother Giovanni Battista became the most direct competitor of his uncle's workshop, the De Rossi alla Pace, now run by his widow along with their children who were then partly still minors [Sons of Giuseppe De Rossi the Elder (1560-1639) and Flaminia Fabio were Giovanni Domenico (1619-1653) Girolamo (born in 1621), Giovanni Giacomo (1627-1691) and Filippo (1631-1656)]. In 1648 Giovanni Giacomo De Rossi, son of Giuseppe, started his own activity in a workshop located “alla Pace”, with the contribution of about 800 plates inherited from his father, whose fund was divided among the four sons. At the death of his elder brother Giovanni Domenico (1653) the part of plates inherited from him was recovered by Giovanni Giacomo, who also took possession of many works of a geographical nature published by his brother. The corpus of works recovered by Giovanni Giacomo consisted of a collection that spanned a chronological span of more than a century, including part of the plates of Salamanca and Lafreri, the workshops of Adamo Scultori, Villamena, Maggi, Carenzano and many others. For the whole course of the century Giovanni Giacomo and his adopted son Domenico (1647-1729) were the point of reference of the Roman publishing industry and increased the chalcographic production of local and artistic character. In addition, in fact, to the works of Giovan Battista Falda we find in the list the engraving matrixes of painters-engravers such as Guido Reni, Giovan Benedetto Castiglione, Giovanni Andrea Podestà and Pietro Testa just to mention the main artists who relied on the De Rossi. When Domenico died in 1729, the printing house was inherited by his son Lorenzo Filippo, who immediately put it up for sale. Pope Clement XII forbade its sale abroad and ordered its appraisal with the intention of purchase by the Apostolic Chamber: the printing house was sold in March 1738 and formed the fund of the newly founded Calcografia Camerale. This act of sale is the document that witnesses the end of the De Rossi printing house, one of the most important European printing houses.
|