

| Reference: | S36168 |
| Author | Claude Du Bosc |
| Year: | 1723 ca. |
| Zone: | Conclave |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 870 x 364 mm |


| Reference: | S36168 |
| Author | Claude Du Bosc |
| Year: | 1723 ca. |
| Zone: | Conclave |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 870 x 364 mm |
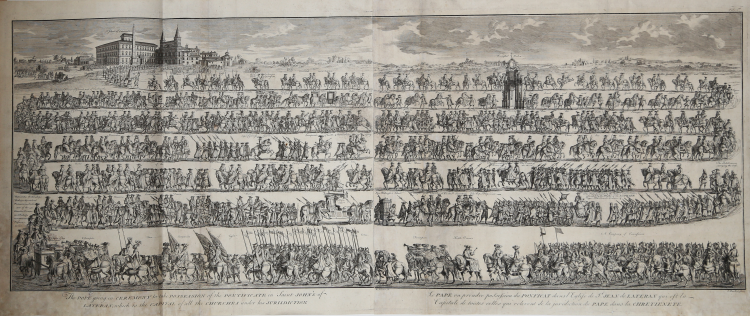
Showing the ceremony to take possession of the Pontificate.
Taken from Bernard Picart "Cérémonies et coutumes religieuses de tous les peuples du monde", appearing from 1723 to 1743.
Etching, some foxing at the bottom corners, otherwise very good.
|
Claude Du Bosc (1682–1745?) was a French engraver who spent much of his career in England. Du Bosc was born in France in 1682. In 1712 he moved to England with Claude Dupuis to assist Nicholas Dorigny in engraving the Raphael cartoons at Hampton Court, where he lived for some time, until the engravings were nearly completed. Dorigny having some disagreement with his assistants, they left him; Dupuis returned to Paris, and Du Bosc set up as an engraver on his own account. He prepared a set of engravings done by himself from the cartoons, but Dorigny's engravings, being superior, held the day.
In February 1714, Du Bosc undertook with Louis Du Guernier to engrave a series of plates illustrative of the battles of the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene. He sent to Paris for two more engravers, Bernard Baron and Beauvais, to assist him on the work, which was completed in 1717.
George Vertue states that towards the end of 1729 Bernard Baron and Du Bosc went over to Paris, Du Bosc wishing to arrange matters relating to the trade of print-selling, as he had now set up a shop, and that Vanloo then painted both their portraits, which they brought back to England.
In 1733 he published an English edition of Bernard Picart's Religious Ceremonies of All Nations, some of the plates being engraved by himself. His other prints included Apollo and Thetis and The Vengeance of Latona, after Jouvenet; some of the Labours of Hercules and The Sacrifice of Iphigenia, after Louis Cheron; The Head of Pompey brought to Cæsar, after B. Picart; The Continence of Scipio, after Poussin; The Temple of Solomon, after Parmentière; a portrait of Bonaventura Giffard, and numerous book illustrations, including numerous plates for Rapin's History of England (1743). Joseph Strutt described him as "an engraver of no great merit", adding that "his style of engraving is coarse and heavy; and the drawing of the naked parts of the figure in his plates is exceedingly defective".
|
|
Claude Du Bosc (1682–1745?) was a French engraver who spent much of his career in England. Du Bosc was born in France in 1682. In 1712 he moved to England with Claude Dupuis to assist Nicholas Dorigny in engraving the Raphael cartoons at Hampton Court, where he lived for some time, until the engravings were nearly completed. Dorigny having some disagreement with his assistants, they left him; Dupuis returned to Paris, and Du Bosc set up as an engraver on his own account. He prepared a set of engravings done by himself from the cartoons, but Dorigny's engravings, being superior, held the day.
In February 1714, Du Bosc undertook with Louis Du Guernier to engrave a series of plates illustrative of the battles of the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene. He sent to Paris for two more engravers, Bernard Baron and Beauvais, to assist him on the work, which was completed in 1717.
George Vertue states that towards the end of 1729 Bernard Baron and Du Bosc went over to Paris, Du Bosc wishing to arrange matters relating to the trade of print-selling, as he had now set up a shop, and that Vanloo then painted both their portraits, which they brought back to England.
In 1733 he published an English edition of Bernard Picart's Religious Ceremonies of All Nations, some of the plates being engraved by himself. His other prints included Apollo and Thetis and The Vengeance of Latona, after Jouvenet; some of the Labours of Hercules and The Sacrifice of Iphigenia, after Louis Cheron; The Head of Pompey brought to Cæsar, after B. Picart; The Continence of Scipio, after Poussin; The Temple of Solomon, after Parmentière; a portrait of Bonaventura Giffard, and numerous book illustrations, including numerous plates for Rapin's History of England (1743). Joseph Strutt described him as "an engraver of no great merit", adding that "his style of engraving is coarse and heavy; and the drawing of the naked parts of the figure in his plates is exceedingly defective".
|